
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Space Laser Communication and Detection Technology, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A specific system structure of down-looking synthetic aperture imaging ladar (SAIL) is given, and a far-field experiment over 6 km of down-looking SAIL under this system design is carried out. The down-looking SAIL can overcome the influence of atmospheric turbulence to a great extent. By applying this system design, it also has advantages in self-compensating phase modulation. A fine image is obtained after aligning in the orthogonal direction and phase error compensation in the travel direction based on a dominant scatterer. The achieved imaging resolutions in the two dimensions are both better than 5 cm.
280.6730 Synthetic aperture radar 280.3640 Lidar 100.2000 Digital image processing 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 082801
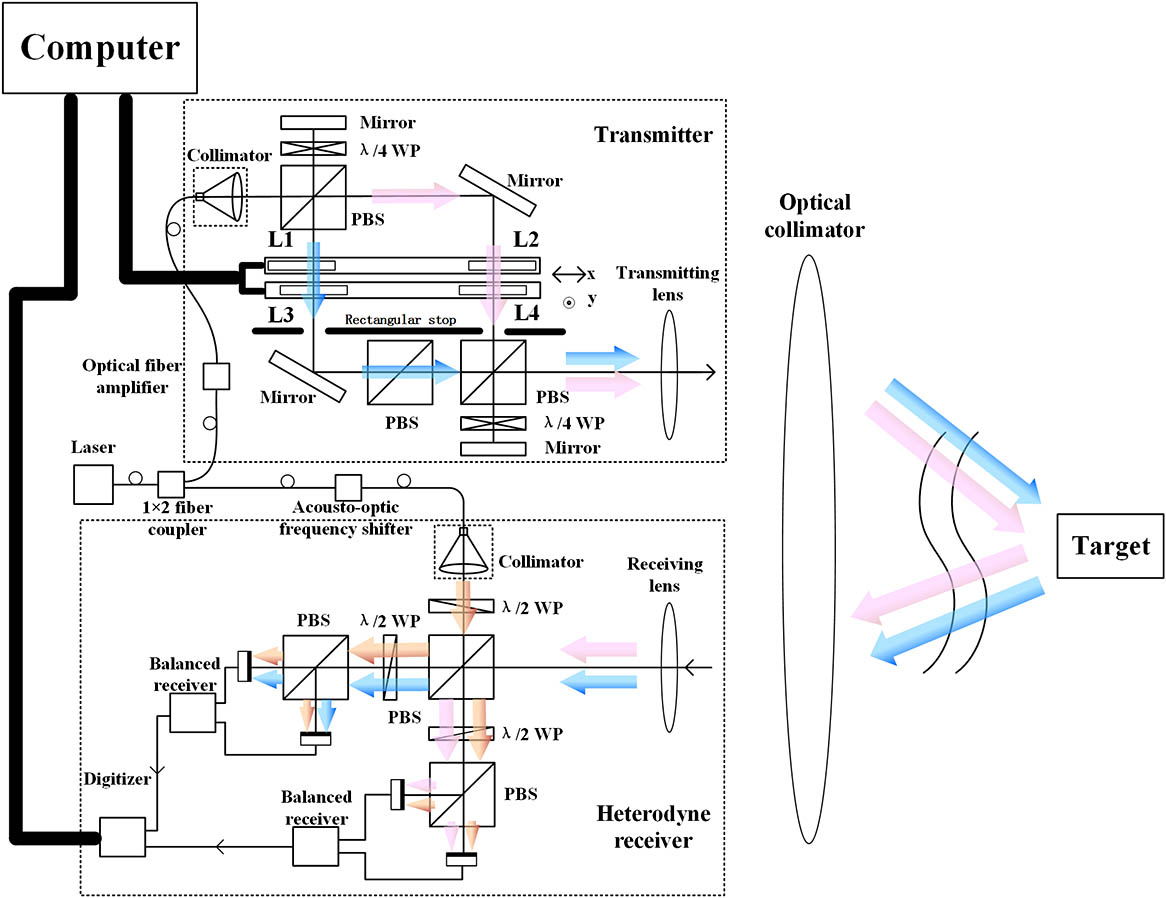
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Space Laser Communication and Detection Technology, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
This Letter gives the general construction of an enhanced self-heterodyne synthetic aperture imaging ladar (SAIL) system, and proposes the principle of image processing. A point target is reconstructed in the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL as well as in down-looking SAIL experiments, and the achieved imaging resolution of the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL is analyzed. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the point target final image in the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL is higher than that in the down-looking SAIL. The enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL can improve the SNR of the target image in far-distance imaging, with practicality.
280.3640 Lidar 280.6730 Synthetic aperture radar 100.2000 Digital image processing 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(10): 102801
中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所空间激光信息传输与探测技术重点实验室, 上海 201800
报道了一个正弦相位调制的大视场机载直视合成孔径激光成像雷达。在室外3.8 km进行了视场扫描并获得了高分辨率合成孔径成像。同时给出了该机载直视合成孔径激光成像雷达的3 km飞行试验结果, 获得了高质量大视场图像, 其成像视场提高了一个量级, 达到了4.8 mrad。
遥感 激光雷达 机载直视合成孔径激光成像雷达 大视场 正弦相位调制
1 上海大学通信与信息工程学院, 上海 200444
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所空间激光信息传输与探测技术重点实验室, 上海 201800
设计了高能激光自主自适应光学系统,利用高能激光的主动照明探测方式对目标进行探测。由于接收到的探测回波光场受散斑效应的影响,因此建立了探测系统的物理模型,具体分析散斑效应的影响。通过散斑光强自相关函数,理论上分析确定了散斑的平均尺度;通过部分相干理论,研究了该系统接收面散斑孔径积分场复相关函数并讨论了不同散斑天线尺度比情况下的积分场复相关函数宽度;分析了目标的成像放大率和理想分辨率,讨论了物像尺度与焦平面光斑尺度之间的关系;通过系统的数值仿真,分析了不同尺度散斑对焦平面光斑阵列的影响;叠加大气湍流,确定了散斑场对大气湍流探测的影响。结果表明散斑尺度介于阵列子孔径和大孔径尺度之间为最佳设计,此时较高的位移测量精度和整体探测率可以兼得。
大气光学 激光散斑 部分相干理论 主动照明 波前探测 自适应光学 光学学报
2016, 36(10): 1001001
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所空间激光信息传输与探测技术重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
用15 m的平行光管模拟远场条件对直视合成孔径激光成像雷达(SAIL)的滑动聚束模式进行了研究。基于单点目标回波收集方程,分析了滑动聚束的信噪比特性,理论和实验证实滑动聚束模式可以通过延长有效采集时间长度的方式提高信噪比。
成像系统 合成孔径激光成像雷达 滑动聚束模式 信噪比

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Space Laser Communication and Detection Technology, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
The electric field distribution in LiNbO3 crystal under different electrode shape is presented by using the digital holographic interferometry. Three configurations of phase modulator including the rectangular electrode type, single-triangle electrode type, and dual-triangle electrode type are performed in this experiment. The nonuniform electric field distribution in these phase modulators are observed and the electric field increases with voltage increasing. The digital holographic interferometry with high electro-optic effect improves the measurement precision. The digital holographic interferometry provides an effective way for studying the electric field distribution. Such in situ quantitative analysis of electric field distribution is a key to optimizing electrode shape.
090.1995 Digital holography 120.2880 Holographic interferometry 120.5050 Phase measurement 120.5475 Pressure measurement Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(2): 020901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Space Laser Communication and Detection Technology, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201800, China
A static-mode synthetic aperture imaging ladar (SAIL) in which the target and carrying platform are kept still during the collection process is proposed and demonstrated. A target point of 0.5 mm×0.5 mm and a two-dimensional (2D) object are reconstructed in the experiments, in which an optical collimator with a focal length of 10 m is used to simulate the far-field condition. The achieved imaging resolution is in agreement with the theoretical design. The static-mode down-looking SAIL has the capability to eliminate the influence from the atmospheric turbulence and can be conveniently operated outdoors.
280.6730 Synthetic aperture radar 280.3640 Lidar 100.2000 Digital image processing 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques 110.0110 Imaging systems Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 042801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Space Laser Communication and Detection Technology, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
We present a tabletop-scale spotlight-mode down-looking synthetic aperture imaging ladar (DL SAIL) demonstrator, which is performed by a collimator with 10 m focal length to simulate the far-field optical field. A specular-point target and a diffuse-reflection target have been used for resolution analysis and 2D imaging, respectively. The experimental result is in agreement with the theoretical design. The experiment setup is capable of simulating a real application scenario for further study. This Letter is focused on the proposition and implementation of spotlight-mode DL SAIL.
100.2000 Digital image processing 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques 110.0115 Imaging through turbulent media 280.6730 Synthetic aperture radar Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(9): 091001
1 华南师范大学广东省微纳光子功能材料与器件重点实验室, 广东 广州 510006
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 中国科学院空间激光信息传输与探测技术重点实验室, 上海 201800
调制技术是影响无线光通信质量的重要因素之一,探索合适的调制方式是无线光通信的内在需要,为此,全面深入分析不同新型组合脉冲调制的性能。详细地分析了脉冲位置调制(PPM)和数字脉冲间隔调制(DPIM)等传统调制方式,以及脉冲位置宽度调制(PPWM)、差分脉冲位置宽度调制(DPPWM)、双幅度脉冲位置调制(DAPPM)和双幅度脉冲间隔调制(DAPIM)等新型组合调制方式的符号结构;全面比较了以上调制方式的平均发射功率和带宽需求;在给定模型下分析了它们的差错性能。数值结果表明:DAPPM 的功率利用率最好,DPPWM 的功率效率最低。当二进制比特位M 取一定值时,PPM 的带宽利用率最低,DPPWM 的带宽利用率最高;随着M 的增加,DAPPM 的带宽效率与DPIM 的带宽效率非常接近。而从差错性能看,在相同的信噪比RSN 条件下,当M 取值一定时,DAPPM 的误包率与PPM 接近,均优于其他组合调制方式,随着M 或RSN 增大,系统误包率逐渐减少;同时,通过增大PPWM的r 参数、减少DAPPM 的α 参数,可适当改善差错性能。因此,要根据实际系统的要求选择合适的调制方式。
无线光通信 调制方式 平均发射功率 带宽需求 误包率
中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所空间激光信息传输与探测技术重点实验室, 上海 201800
提出了一种双曲波前差自扫描直视合成孔径激光成像雷达系统,结构上采用正交偏振同轴双光束发射和偏振干涉自差探测结构,原理上应用波面变换产生双曲波前差照射光斑,因此通过目标的相对运动在交轨向自动扫描产生目标面横向距离有关的线性相位调制,同时在顺轨向产生目标顺轨向距离有关的二次项相位历程,采用补偿二次多普勒频移的傅里叶变换和补偿交叉耦合的共轭二次项匹配滤波算法实现图像重构。本系统主要特点是结构简单,无需使用任何光调制器,没有交轨向信号的初始相位同步问题,不存在目标时间延时影响,同时也保留了直视合成孔径激光成像雷达的固有优点,如有效地降低了大气等相位干扰,照明光斑可以很大,接收口径可以很大。本雷达适用于航空航天的各种相对运动速度和作用距离的对地观察成像和基于逆合成孔径原理的激光成像雷达。
遥感 合成孔径激光成像雷达 直视合成孔径激光成像雷达 波面变换 双曲波面 自动扫描线性相位调制





